essential-skill-for-study
Why do we learn ?
- to gather info
- to learn info
- to check for understanding
- to refresh ourselves
- improve our learning / study skills.
How do we learn?
- visual - image/video/graph
- auditory - audio/ vocal/ saying loud
- Kinesthetic - learn by doing
acrostics
features
- Sequence of letter
- make a poem or sentence
- 1st letter help you remember
example - to learn all planets name sequentially
My Very Excellent Mother Just Served Us Nothing
M - Mercury
V - Venus
E - Earth
M - Mars
J - Jupiter
S - Saturn
U - Uranus
N - Neptune
example - treble clip for music students
Every good boy deserved fun(EGBDF)
example - trigonometry
Sausages only half cooked are harmful to our appetites
Sin = Opposite / hypotenuse
cos = Adjacent / hypotenuse
Sin = Opposite / Adjacent
Acronyms
IPMAT - the stage of cell division
I - Interphase
P - Prophase
M - Metaphase
A - Anaphase
T - Telophase
BEDMAS - right order of math operation
B - Brackets
E - Exponents
D - Division
M - Multiplication
A - Addition
S - Subtraction
HOMES - Great Lake in America
H - Huron
R - Ontario
M - Michigan
E - Erie
S - Superior
Analogies
Comparison between unlike things that has something in common.
This sentences contain following
"it's like as"
"it's same as"
"think of it as"
Mnemonics - organizing and memorizing info
It has 3 principle
- Imagination
- Association
- Location
Reading
- Speed
- relax
- focus
- use ruler / card / pen to guide eyes
- force eyes to keep up
- don’t fixate one each word.
- Skim
- General Idea / gist / overview of each paragraph
- More info in less time
- Read first and last bit of each section
- See where its going / what it covers
- Scan - like phonebook
- read quickly for specific info
- use heading title formatting etc
- don’t read every word
- don’t aiming to understand everything
Keywords
large amount of content remember by single word
Tree diagram - possible outcome from a event
- relationship
- genealogy (family history)
- faults
- organization chart ( like employee hierarchy )
- WBS(work breakdown structure )
spider diagram
Complex topic in one page. Its kind of bird’s eye view.
mind maps
- generate idea and association
- Visually organize info
- Main concept in middle
- additional information can add easily
- we can use image, words, idea, fun
concept diagram
Relationship - ideas, images, words
- Everything connect
- Logical thinking
- Enhance meaningful learning
CUE - Flash cards
- One side contain keyword / Question
- Other side contain Answer / Explanation
Note taking - Skeleton system
Skeleton is suitable for books, article, number of point, paragraph, sequential building
9 techniques are following
- re-read big picture
- re-write connection / relationship
- Question yourself what you’ve written
- Ask “Do I understand this?”
- Is info consistent
- Look for additional info
- Do symbols and abbreviation make sense
- Highlight important word or concept
- condense: diagram, color, image, keywords
cons of Skeleton approach is
- difficult to add or amend
- don’t show connection / relationship
- easy to copy verbatim & not understand
Note taking - Cornell Note taking system
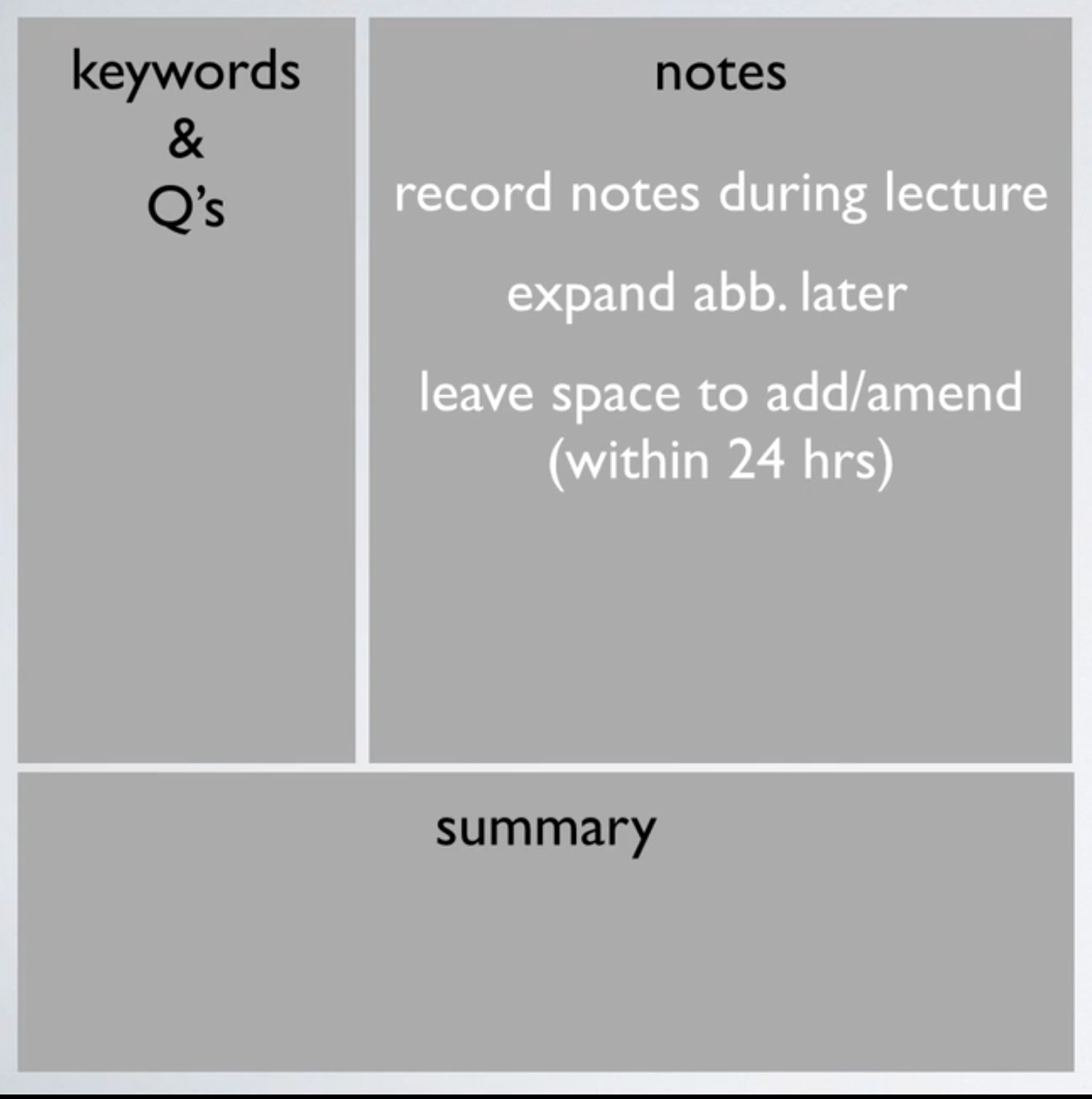
People refereed as “Do it right 1st time method”
- structured and common sense
- clear note you can engage with
- clear material to revise from
- aids to recall
Pros:
- clear set of condensed key ideas
- can be used in lectures
- engagement and recall material
- note will be become valuable study resource
studying from book using PQRST and SQ3R method
Technique of PQRST
- Preview - skim major headlines / pints
- Question - formulate
- Read material that relate to Q’s
- Summarize
- Test your ability to answer Q’s
Pros of PQRST
- Directly relate to questions
- Adaptable
- Practice timing
- Potential to preempt Q’s
Technique of SQ3R
- Survey - general gist / big to small
- Question yourself - active process - why, what ( like what I already know about this subject )
- Read - Skim preview, again notes, look for answer
- Recall - Think, assimilate, recall
- Review -
- Do you understand ?
- Did you identify all main points ?
- are there gaps ?
Triple strength of learning
- See
- Hear
- Say
Quadruple strength of learning
- See
- Hear
- Say
- Write
Prioritization - traffic light approach (gor - essential - desirable - limitless time)

green - essential - study first
Essential to know (for exam). Should be studied 1st fundamental concept maybe 1st on a syllabus
orange - desirable
Important but time consuming
Red - Limitless time
lowest priority - complex topic / low return
Method of Loci -
come from word locus. locus = place
- Invest time to practice
- Immerse yourself in the place
- Active not passive
- Familiar to obscure
- Need emotional / visual images - not boring
- Consider smell and noises as well
Peg / Hook
Associate 1 - 10 with words that rhyme
Associate words with info to remember
- bun
- shoe
- tree
- door
- hive
- sticks
- heaven
- gate
- wine
- hen
example - world is the third planet in solar system. It contains lot of tree. so we can rhymes with three earth holding tree
Auditory approach
- Talking out loud
- Ask questions
- Group discussion
- Use word association
Don’t miss anything - BRG
Founded by Royal Literary fund. Every part of Q is considered.
- Black - BLAtant instructions (Must be done)
- Red - REquired / Reference ( input of some sort of definition, terms, author, theories etc)
- Green - GREmlins / GREen light (Signal you might miss or hint)
Don’t miss anything - PEE
to make a great paragraph
- Makes a Point
- Provide Evidence
- Include Explanation, Examples,
- Evaluations what you wrote earlier
Consider
- having space after paragraph ( it will help you to add additional info later)
- add additional info
- signal moving into next point
- ease of reading
a general strategy - ASPIRE
A - approach / attitude / arrange
- approach with +ve attitude
- arrange schedules
- limit distraction
S - select / survey / scan
- select block of material to study
- survey, heading, graphics & Q’s (overview)
- Scan for keyword
- mark what you don’t understand
P - Piece together the parts
- Put books and notes to one side
- Piece together what you’ve studied
- Piece together what you’ve understand
I - investigate, inquire, inspect
- Investigate alternative source of info
- Inquire from other sources, Prof, experts.
- Inspect what you don’t understand ( please be honest with you)
R - Reexamine, Reflect, Relay
- Re-examine what question do I still need to ask
- Re-examine am I missing something
- Reflect on how you can apply this info
Case study - learning plants cell
A plant cell like a school
- Cell wall - Protective school walls
- Cell membrane - School door letting things in and out
- cytoplasm - air surrounding everything
- Chloroplasts - Canteen - where food is made
- mitochondria - football field - food converted into energy
- nucleus - head master room - control center
- nucleolus - copy machine - where DNA is copied
summary 2 is very important - more about