1 - Basic syntax
$(selector).action()
2 - The Document Ready Event
$(document).ready(function(){
// jQuery methods go here...
});
// shorter
$(function(){
// jQuery methods go here...
});
3 - Selects the first <li> element of the first <ul>
$("ul li:first")
4 - Selects the first <li> element of every <ul>
$("ul li:first-child")
5 - Selects all <a> elements with a target attribute value equal to "_blank"
$("a[target='_blank']")
6 - Selects all <a> elements with a target attribute value NOT equal to "_blank"
$("a[target!='_blank']")
6 - Selects all <button> elements and <input> elements of type="button"
$(":button")
7 - Mouse Events
- click
- dblclick
- mouseenter
- mouseleave
- mousedown
- mouseup
- hover (combination of mouseenter and mouseleave)
8 - Keyboard Events
- keypress
- keydown
- keyup
- blur
9 - Form Events
- submit
- change
- focus (attaches an event handler function to an HTML form field)
10 - Document/Window Events
- load
- resize
- scroll
- unload
11 - Click method
$("p").click(function(){
$(this).hide();
});
12 - The on() Method
The on() method attaches one or more event handlers for the selected elements.
$("p").on("click", function(){
$(this).hide();
});
13 - multiple event handlers to a single element:
$("p").on({
mouseenter: function(){
$(this).css("background-color", "lightgray");
},
mouseleave: function(){
$(this).css("background-color", "lightblue");
},
click: function(){
$(this).css("background-color", "yellow");
}
});
14 - hide in jquery
$(selector).hide(speed,callback);
$("button").click(function(){
$("p").hide(1000);
});
15 - show in jquery
$(selector).show(speed_optional,callback_optional);
$("button").click(function(){
$("p").hide(1000);
});
16 - jQuery toggle()
combination of hide() and show() method
$(selector).toggle(speed,callback);
$("button").click(function(){
$("p").toggle();
});
17 - jquery fade method
- fadeIn() show the content
- fadeOut() hide the content
- fadeToggle()
- fadeTo()
//syntax for fadeIn, fadeOut, fadeToggle
$(selector).fadeIn(speed,callback);
//syntax for fadeTo which taking 3 parameters
$(selector).fadeTo(speed,opacity,callback);
18 - jQuery Effects - Sliding
- slideDown() show the content
- slideUp() hide the content
- slideToggle()
$(selector).slideDown(speed,callback);
$("#flip").click(function(){
$("#panel").slideDown();
});
19 - jQuery Animations - The animate() Method
$(selector).animate({params},speed,callback);
$("button").click(function(){
$("div").animate({
left: '250px',
opacity: '0.5',
height: '150px',
width: '150px'
});
});
20 - jQuery animate() method with relative value +=
$("button").click(function(){
$("div").animate({
left: '250px',
height: '+=150px',
width: '+=150px'
});
});
21 - jQuery animate() - Using Pre-defined Values
$("button").click(function(){
$("div").animate({
height: 'toggle'
});
});
22 - jQuery animate() - Uses Queue Functionality
if you write multiple animate() calls after each other, jQuery creates an “internal” queue with these method calls. Then it runs the animate calls ONE by ONE.
$("button").click(function(){
var div = $("div");
div.animate({height: '300px', opacity: '0.4'}, "slow");
div.animate({width: '300px', opacity: '0.8'}, "slow");
div.animate({height: '100px', opacity: '0.4'}, "slow");
div.animate({width: '100px', opacity: '0.8'}, "slow");
});
23 - jQuery stop() Method
The jQuery stop() method is used to stop an animation or effect before it is finished.
/**
* stopAll parameter specifies whether also the
* animation queue should be cleared or not.
* Default is false, which means that only
* the active animation will be stopped,
* allowing any queued animations to be
* performed afterwards.
*
*
* The optional goToEnd parameter
* specifies whether or not to complete
* the current animation immediately.
* Default is false.
*
*/
$(selector).stop(stopAll,goToEnd);
$("#stop").click(function(){
$("#panel").stop();
});
24 - jQuery Method Chaining
there is a technique called chaining, that allows us to run multiple jQuery commands, one after the other, on the same element(s)
$("#p1").css("color", "red").slideUp(2000).slideDown(2000);
//prettier format following - which should be preferred
$("#p1").css("color", "red")
.slideUp(2000)
.slideDown(2000);
24 - Get Content from HTML page
- text() - Sets or returns the text content of selected elements
- html() - Sets or returns the content of selected elements (including HTML markup)
- val() - Sets or returns the value of form fields
25 - how to get content with the jQuery text() and html() methods
alert("Text: " + $("#test").text());
alert("HTML: " + $("#test").html());
26 - how to get the value of an input field with the jQuery val()
<input type="text" id="test" value="Mickey Mouse"></p>
$("button").click(function(){
alert("Value: " + $("#test").val());
});
27 - Get Attributes - attr()
The jQuery attr() method is used to get attribute values.
alert($("#w3s").attr("href"));
28 - Set Content - text(), html(), and val()
- text() - Sets or returns the text content of selected elements
- html() - Sets or returns the content of selected elements (including HTML markup)
- val() - Sets or returns the value of form fields ~~~js $(“#test2”).html(”Hello world!”); ~~~
29 - A Callback Function for text(), html(), and val()
All of the three jQuery methods above: text(), html(), and val(), also come with a callback function. The callback function has two parameters: the index of the current element in the list of elements selected and the original (old) value. You then return the string you wish to use as the new value from the function.
$("#test1").text(function(i, origText){
return "Old text: " + origText + " New text: Hello world! (index: " + i + ")";
});
30 - Set Attributes - attr()
$("#w3s").attr("href", "https://www.w3schools.com/jquery/");
// set multiple attribute using attr method
$("#w3s").attr({
"href" : "https://www.w3schools.com/jquery/",
"title" : "W3Schools jQuery Tutorial"
});
31 - A Callback Function for attr()
$("#w3s").attr("href", function(i, origValue){
return origValue + "/jquery/";
});
32 - Add Elements
- append() - Inserts content at the end of the selected elements
- prepend() - Inserts content at the beginning of the selected elements
- after() - Inserts content after the selected elements
- before() - Inserts content before the selected elements
~~~js
$(“p”).append(“Some appended text.”);
function appendText() {
var txt1 = “
Text.
”; // Create element with HTML var txt2 = $(””).text(“Text.”); // Create with jQuery var txt3 = document.createElement(“p”); // Create with DOM txt3.innerHTML = “Text.”; $(“body”).append(txt1, txt2, txt3); // Append the new elements } ~~~
33 - Remove Elements
- remove() - Removes the selected element (and its child elements)
- empty() - Removes the child elements from the selected element ~~~js $(“#div1”).remove(); $(“#div1”).empty(); ~~~
34 - jQuery Manipulating CSS
- addClass() - Adds one or more classes to the selected elements
- removeClass() - Removes one or more classes from the selected elements
- toggleClass() - Toggles between adding/removing classes from the selected elements
- css() - Sets or returns the style attribute
$("button").click(function(){
$("h1, h2, p").addClass("blue");
$("div").addClass("important");
// multiple class by giving space
$("#div1").addClass("important blue");
// remove class
$("h1, h2, p").removeClass("blue");
});
35 - jQuery - css()
The css() method sets or returns one or more style properties for the selected elements.
// return propertyname
css("propertyname");
//set property name
css("propertyname","value");
$("p").css("background-color", "yellow");
36 - Set Multiple CSS Properties
css({"propertyname":"value","propertyname":"value",...});
$("p").css({"background-color": "yellow", "font-size": "200%"});
37 - jQuery Dimension Methods
- width()
- height()
- innerWidth()
- innerHeight()
- outerWidth()
- outerHeight()
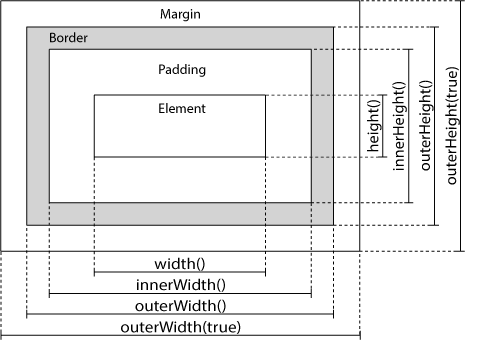
38 - jquery width and height method
- The width() method sets or returns the width of an element (excludes padding, border and margin).
- The height() method sets or returns the height of an element (excludes padding, border and margin).
$("button").click(function(){
var txt = "";
txt += "Width: " + $("#div1").width() + "</br>";
txt += "Height: " + $("#div1").height();
$("#div1").html(txt);
});
39 - jQuery innerWidth() and innerHeight() Methods
- The innerWidth() return (elementWidth + padding)
- The innerHeight() return (elementHeight + padding)
$("button").click(function(){
var txt = "";
txt += "Inner width: " + $("#div1").innerWidth() + "</br>";
txt += "Inner height: " + $("#div1").innerHeight();
$("#div1").html(txt);
});
40 - jQuery outerWidth() and outerHeight() Methods
- The outerWidth() return (elementWidth + padding + border)
- The outerHeight()return (elementHeight + padding + border)
- The outerWidth(true) return (elementWidth + padding + border + margin)
- The outerHeight(true)return (elementHeight + padding + border + margin)
var txt = "Outer height: " + $("#div1").outerHeight();
var txt = "Outer height: " + $("#div1").outerHeight(true);
41 - document and window width
$(document).width()
$(document).height()
$(window).width()
$(window).height()
42 - sets the width and height of a specified <div> element:
$("button").click(function(){
$("#div1").width(500).height(500);
});
43 - What is Traversing?
jQuery traversing, which means “move through”, are used to “find” (or select) HTML elements based on their relation to other elements. Start with one selection and move through that selection until you reach the elements you desire.
44 - jQuery Traversing - Ancestors
An ancestor is a parent, grandparent, great-grandparent, and so on. * parent() * parents() * parentsUntil()
45 - jQuery parent()
The parent() method returns the direct parent element of the selected element. This method only traverse a single level up the DOM tree.
$("span").parent();
46 - jQuery parents() Method
The parents() method returns all ancestor elements of the selected element, all the way up to the document’s root element (<html>).
$("span").parents();
$("span").parents("ul");
47 - jQuery parentsUntil() Method
The parentsUntil() method returns all ancestor elements between two given arguments.
The following example returns all ancestor elements between a <span> and a <div> element
$("span").parentsUntil("div");
48 - jQuery Traversing - Descendants
A descendant is a child, grandchild, great-grandchild, and so on. * children() * find()
49 - jQuery children() Method
The children() method returns all direct children of the selected element. This method only traverse a single level down the DOM tree.
$("div").children();
You can also use an optional parameter to filter the search for children.
The following example returns all <p> elements with the class name “first”, that are direct children of <div>:
$("div").children("p.first");
50 - Query find() Method
The find() method returns descendant elements of the selected element, all the way down to the last descendant.
The following example returns all <span> elements that are descendants of <div>
$("div").find("span");
The following example returns all descendants of <div>
$("div").find("*");
51 - Traversing Sideways in The DOM Tree
- siblings()
- next()
- nextAll()
- nextUntil()
- prev()
- prevAll()
- prevUntil()
(next, nextAll, nextAll) sounds like (parent, parents, parentsUntil)
52 - jQuery siblings() Method
The siblings() method returns all sibling elements of the selected element.
The following example returns all sibling elements of <h2>
$("h2").siblings();
You can also use an optional parameter to filter the search for siblings.
The following example returns all sibling elements of <h2> that are <p> elements
$("h2").siblings("p");
53 - jQuery next() Method
The next() method returns the next sibling element of the selected element.
The following example returns the next sibling of <h2>
$("h2").next();
54 - jQuery nextAll() Method
The nextAll() method returns all next sibling elements of the selected element.
The following example returns all next sibling elements of <h2>
$("h2").nextAll();
55 - jQuery nextUntil() Method
The nextUntil() method returns all next sibling elements between two given arguments.
The following example returns all sibling elements between a <h2> and a <h6> element
$("h2").nextUntil("h6");
56 - jQuery prev(), prevAll() & prevUntil() Methods
The prev(), prevAll() and prevUntil() methods work just like the methods (next, nextAll, nextUntil) but with reverse functionality: they return previous sibling elements (traverse backwards along sibling elements in the DOM tree, instead of forward).
57 - jQuery Traversing - Filtering
- first()
- last()
- eq()
- filter()
- not()
The most basic filtering methods are first(), last() and eq(), which allow you to select a specific element based on its position in a group of elements. Other filtering methods, like filter() and not() allow you to select elements that match, or do not match, a certain criteria.
58 - jQuery first() Method
The first() method returns the first element of the specified elements.
The following example selects the first <div> element
$("div").first().css("background-color", "yellow");
59 - jQuery last() Method
The last() method returns the last element of the specified elements.
The following example selects the last <div> element
$("div").last().css("background-color", "yellow");
60 - jQuery eq() method
The eq() method returns an element with a specific index number of the selected elements. The index numbers start at 0, so the first element will have the index number 0 and not 1. The following example selects the second
element (index number 1):
$("p").eq(1).css("background-color", "yellow");
61 - jQuery filter() Method
The filter() method lets you specify a criteria. Elements that do not match the criteria are removed from the selection, and those that match will be returned.
The following example returns all <p> elements with class name “intro”:
$("p").filter(".intro").css("background-color", "yellow");
62 - jQuery not() Method ( opposite of filter method )
The not() method returns all elements that do not match the criteria.
The following example returns all <p> elements that do not have class name “intro”:
$("p").not(".intro").css("background-color", "yellow");
63 - jQuery - AJAX load() Method
The jQuery load() method is a simple, but powerful AJAX method.
$(selector).load(URL,data,callback);
It is also possible to add a jQuery selector to the URL parameter.
The following example loads the content of the element with id="p1", inside the file “demo_test.txt”, into a specific <div> element
$("#div1").load("demo_test.txt #p1");
The optional callback parameter specifies a callback function to run when the load() method is completed. The callback function can have different parameters: * responseTxt - contains the resulting content if the call succeeds * statusTxt - contains the status of the call * xhr - contains the XMLHttpRequest object
$("button").click(function(){
$("#div1").load("demo_test.txt", function(responseTxt, statusTxt, xhr){
if(statusTxt == "success") {
alert("External content loaded successfully!");
}
if(statusTxt == "error") {
alert("Error: " + xhr.status + ": " + xhr.statusText);
}
});
});
64 - jQuery $.get() Method
The $.get() method requests data from the server with an HTTP GET request.
$.get(URL,callback);
$.get("demo_test.asp", function(data, status){
alert("Data: " + data + "\nStatus: " + status);
});
65 - jQuery $.post() Method
The $.post() method requests data from the server using an HTTP POST request.
$.post(URL,data,callback);
$("button").click(function(){
$.post("demo_test_post.asp",
{
name: "Donald Duck",
city: "Duckburg"
},
function(data, status){
alert("Data: " + data + "\nStatus: " + status);
});
});
66 - jQuery noConflict() Method
The noConflict() method releases the hold on the $ shortcut identifier, so that other scripts can use it.
You can of course still use jQuery, simply by writing the full name instead of the shortcut:
$.noConflict();
jQuery(document).ready(function(){
jQuery("button").click(function(){
jQuery("p").text("jQuery is still working!");
});
});
The noConflict() method returns a reference to jQuery, that you can save in a variable, for later use.
var jq = $.noConflict();
jq(document).ready(function(){
jq("button").click(function(){
jq("p").text("jQuery is still working!");
});
});
If you have a block of jQuery code which uses the $ shortcut and you do not want to change it all, you can pass the $ sign in as a parameter to the ready method
$.noConflict();
jQuery(document).ready(function($){
$("button").click(function(){
$("p").text("jQuery is still working!");
});
});
67 - a list filter
<input id="myInput" type="text" placeholder="Search..">
<br>
<ul id="myList">
<li>First item</li>
<li>Second item</li>
<li>Third item</li>
<li>Fourth</li>
</ul>
$("#myInput").on("keyup", function() {
var value = $(this).val().toLowerCase();
$("#myList li").filter(function() {
$(this).toggle($(this).text().toLowerCase().indexOf(value) > -1)
});
});
68 - a table filter
<input id="myInput" type="text" placeholder="Search..">
<br>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Firstname</th>
<th>Lastname</th>
<th>Email</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody id="myTable">
<tr>
<td>John</td>
<td>Doe</td>
<td>john@example.com</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Anja</td>
<td>Ravendale</td>
<td>a_r@test.com</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
$("#myInput").on("keyup", function() {
var value = $(this).val().toLowerCase();
$("#myTable tr").filter(function() {
$(this).toggle($(this).text().toLowerCase().indexOf(value) > -1)
});
});
69 - filter anything inside a div
<input id="myInput" type="text" placeholder="Search..">
<div id="myDIV">
<p>I am a paragraph.</p>
<div>I am a div element inside div.</div>
<button>I am a button</button>
<button>Another button</button>
<p>Another paragraph.</p>
</div>
$("#myInput").on("keyup", function() {
var value = $(this).val().toLowerCase();
$("#myDIV *").filter(function() {
$(this).toggle($(this).text().toLowerCase().indexOf(value) > -1)
});
});